X chromosome compaction is not disrupted in condensin I or II depleted Biology Diagrams Similarly to bulky chromosome bridges, they can be visualized by DAPI staining and revealed in cells transiting anaphase. They are mainly associated with defects intrinsic to mitosis such as abnormal microtubule-kinetochore attachments, centrosome amplification, aberrant spindle assembly checkpoint, and defects in sister chromatid cohesion.

We found that primary HeH frequently have severe cohesion defects in metaphase chromosomes that are associated with increased chromosomal copy number heterogeneity, indicating that a subset of HeH ALL may possibly harbor CIN. Our data point to a novel opportunity for targeted therapy in HeH ALL, in line with other cancers with cohesion defects.

Sister Chromatid Cohesion, Chromosome ... Biology Diagrams
Defects in sister chromatid cohesion or cohesion dissolution will lead to aneuploidy and chromosome instability (CIN). Mutations or misregulation of cohesin subunits, or cohesion-related genes have been implicated in cancers, cohesinopathies, neurological diseases and aneuploid oocytes observed in maternal ageing. We further conclude that aberrant RAD21 expression is a strong candidate to underlie aberrant cohesion, chromosome instability and contribute to the development of the disease. Our findings support a growing body of evidence suggesting that cohesion defects and aberrant RAD21 expression are pathogenic events that contribute to tumor development.
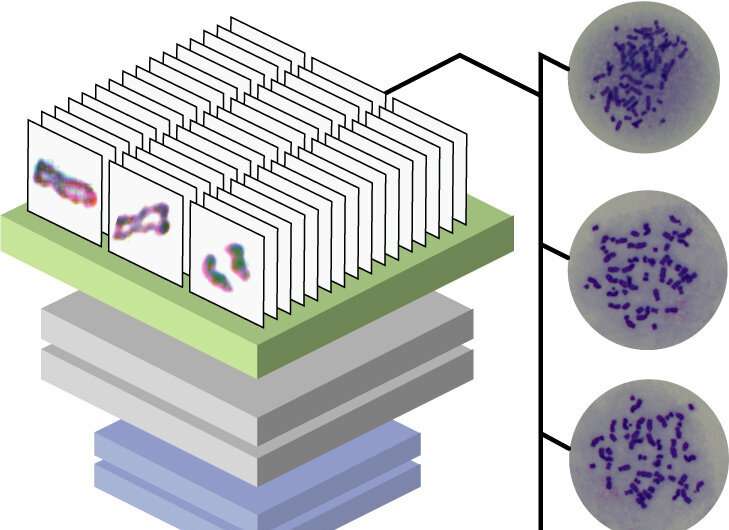
Aneuploidy is a recurring hallmark in many cancer types, and abnormalities in chromosomal cohesion and separation have been identified as significant contributors to various cancers, such as acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, colorectal, bladder, and other solid cancers. Hirano T. Chromosome cohesion, condensation, and Chromosome cohesion is established during S phase (when the chromosomes are replicated) and is then dissolved completely in metaphase to allow sister chromatids to come apart. The dissolution of cohesion is highly regulated; human cell lines that have defects in the regulation of cohesion show the hallmarks of cancer cells .
Sister chromatid cohesion defects are associated with ... Biology Diagrams
Similarly, CDC4 was known to play a role in chromosome stability and to have a variety of other functions, but there were no previous data linking CDC4 mutations to cohesion defects. Our study demonstrates that down-regulation of these genes leads to cohesion defects in human cells, and also identifies somatic mutations in human cancers in First, sister chromatids are resolved from each other while both sister chromatid cohesion and DNA catenation are removed (sister chromatid resolution). Second, each chromatid is folded both axially and laterally (chromosome folding). We found that, whereas 16% of NCAPD2-Cer control cells showed defects in chromosome segregation (categories