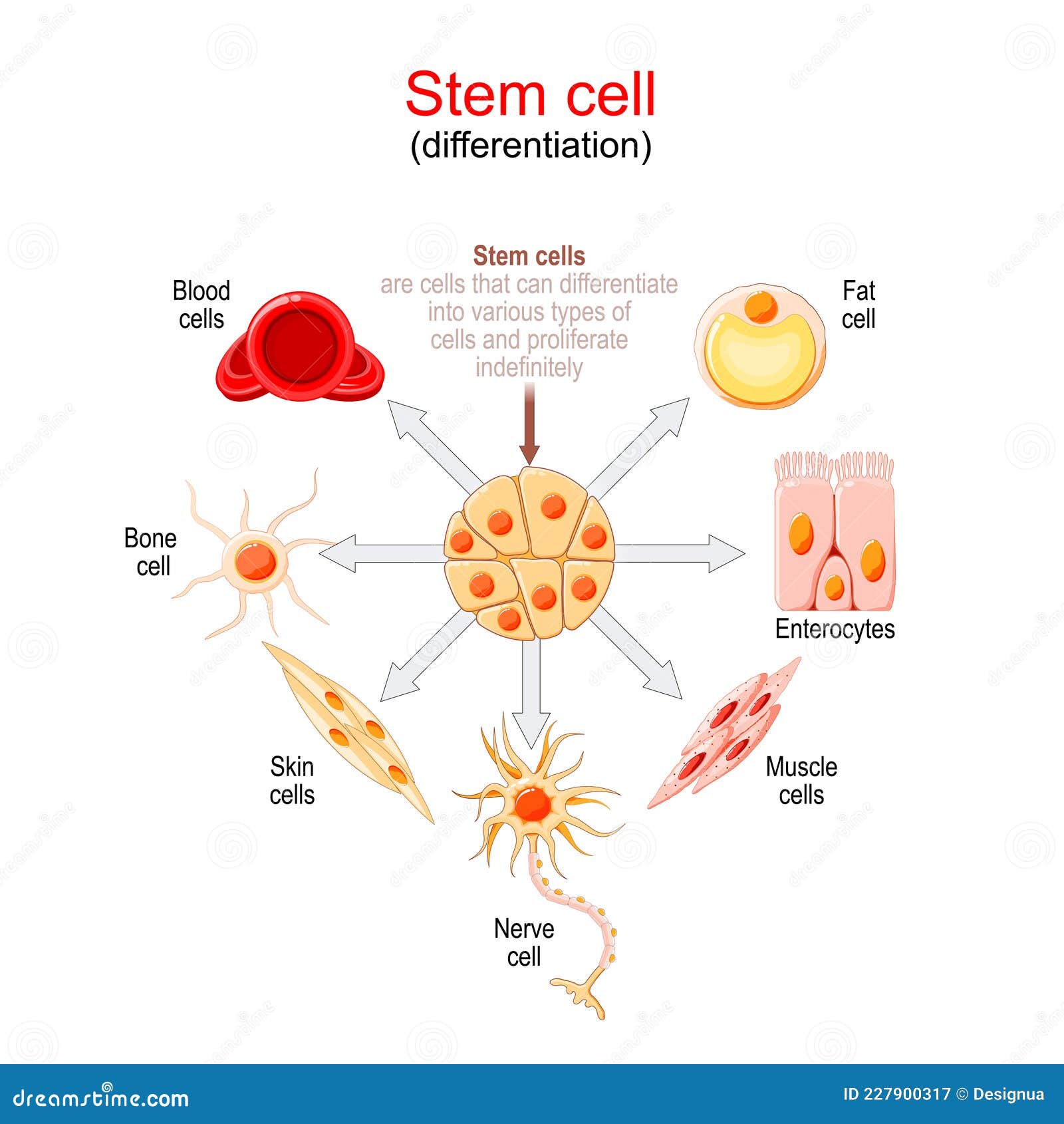
Three dimensional render of stem cell mitosis Stock Photo Picture And Biology Diagrams The Significance of Stem Cells. A stem cell is a cell that can divide (by mitosis) an unlimited number of times. Each new cell (produced when a stem cell divides) has the potential to remain a stem cell or to develop into a specialised cell such as a blood cell or a muscle cell. Developing into a specialised cell occurs through a process known as differentiation Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) are self-renewing and pluripotent cells that originate from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. Mitosis is fundamental to organism survival and reproduction and is responsible for the equal distribution of duplicated chromosomes into daughter cells. Mitotic dysf …

Importantly, quiescence is a relative concept rather than an absolute measure, as also quiescent stem cells inevitably undergo mitosis. Quiescent cells are traditionally identified through long-term DNA (or chromatin) label retention and are hence referred to as label-retaining cells (LRCs). Of note, the various protocols will not only label Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images. Before a dividing cell enters mitosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. About 90% of a cell's time in the normal cell cycle may be spent in interphase.. G1 phase: The period before the synthesis of DNA.In this phase, the cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. Stem Cells _____ Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or become another type of cell with a more specialized function. All stem cells—regardless of their source—have three special properties: 1.

The specialized mitotic behavior of human embryonic stem cells Biology Diagrams
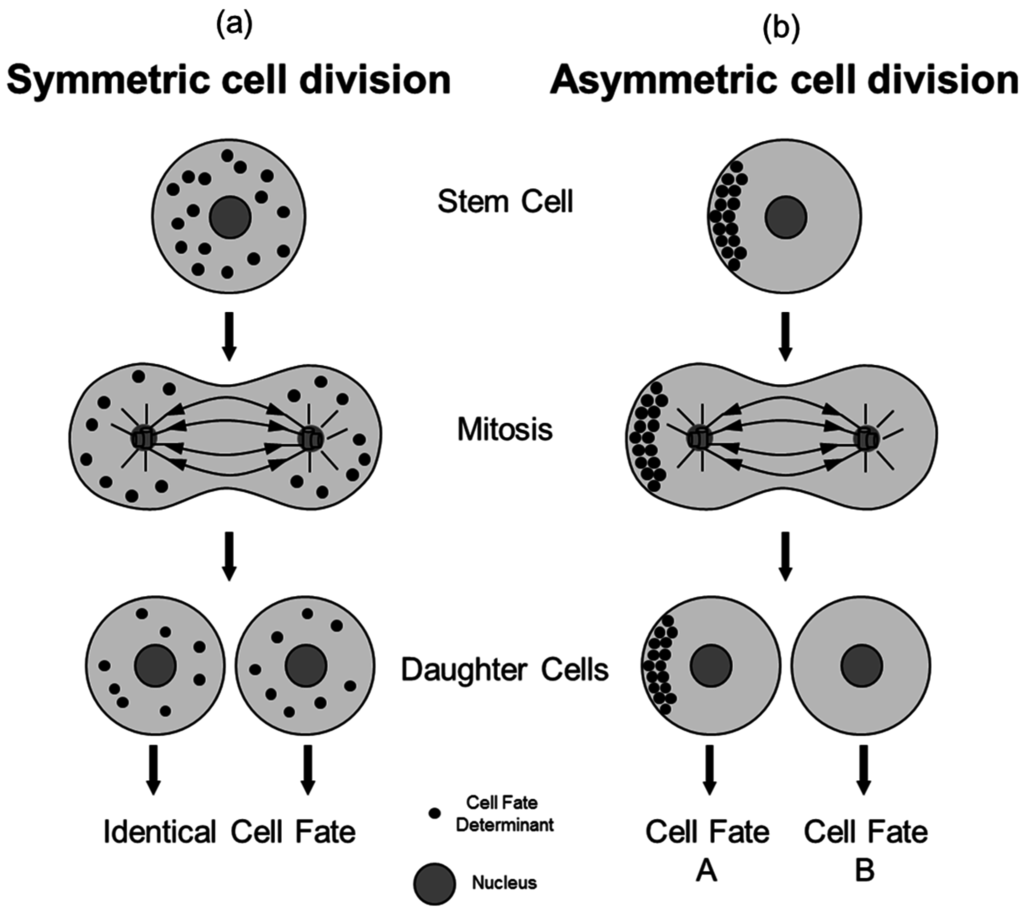
Mitosis is a type of cell division which ensures that, when a cell divides, each new cell produced has the same genetic information. Each human body cell contains 46 chromosomes. These can be When a stem cell divides, the resulting two daughter cells may be: 1) both stem cells, 2) a stem cell and a more differentiated cell, or 3) both more differentiated cells. What controls the balance between these types of divisions to maintain stem cells at an appropriate level within a given tissue is not yet well known.
Biotin is an essential vitamin that humans and flies acquire from their food and microbiota. Neophytou and Pitsouli show that, in flies, biotin and its transporter, Smvt, function in intestinal stem cells to control mitosis, infection-induced regeneration, and tumorigenesis. Upon dietary biotin scarcity, biotin-producing microbiota can rescue reduced intestinal mitosis.
STEM Cell Information - National Institutes of Health Biology Diagrams
Duration of mitosis. The advantage of imaging living cells without perturbing them with chemicals is that we can make observations on their natural dynamics. For example, we can determine the duration of the different phases in mitosis in this line of mouse embryonic stem cells. The selected frames are 1min 30s apart and the time is indicated

undergo mitosis. Stem cells do divide by mitosis and this makes them very important for replacing lost or damaged specialized cells. 2) Should mitosis be discussed, you may wish to note the following: In mitosis, the DNA in the daughter cells is identical to the DNA in the dividing cell.