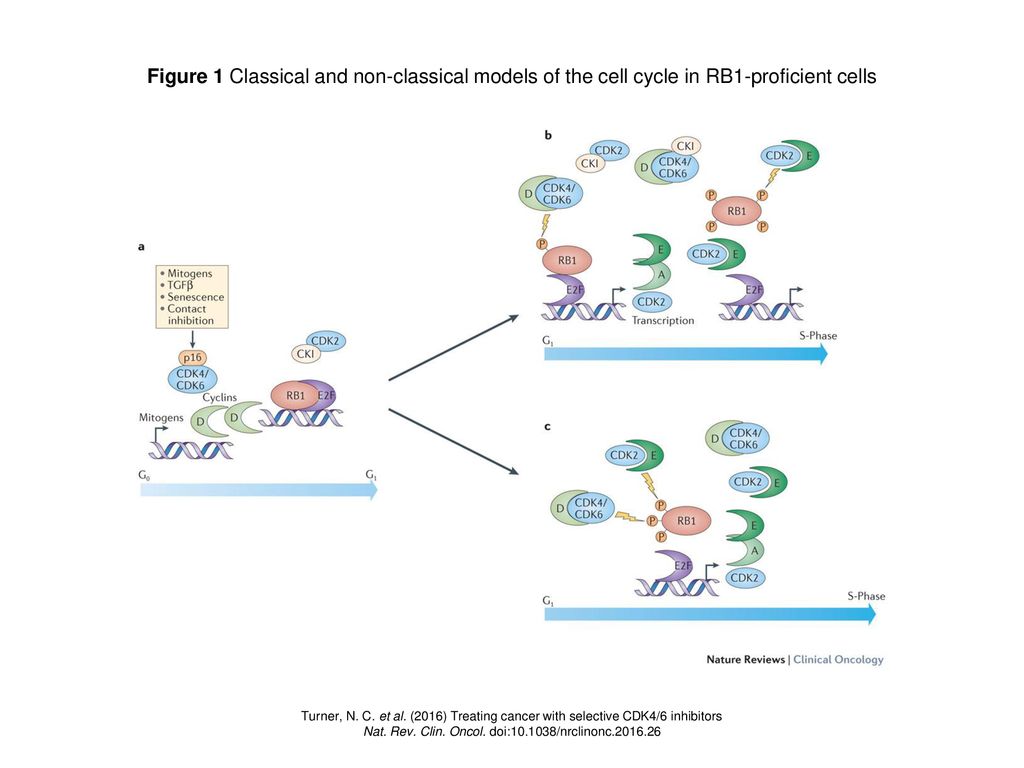
Rb gene and cell cycle Biology Diagrams The RB gene was cloned more than 25 years ago 1.Since that time, its encoded protein has been identified as a universal cell cycle regulator with a central role in controlling the commitment of a cell to initiate DNA replication and divide 2.Eliminating RB function allows unregulated cell cycle progression and promotes tumour growth. Key Regulatory Proteins. Cell cycle progression is controlled by regulatory proteins that act as molecular switches, responding to internal and external signals to either promote or halt division. Phosphorylation of Rb by cyclin-CDK complexes releases this inhibition, allowing progression. If DNA damage is detected, p53 activates p21, which Deletion of Rb protein in the small intestine enterocytes resulted in ectopic cell cycle reentry and while these cells had a higher rate of apoptosis, the remainder of the cycling cells did not completely differentiate which may lead to the continued proliferation of the undifferentiated cells . Therefore, inactivation of Rb in the small
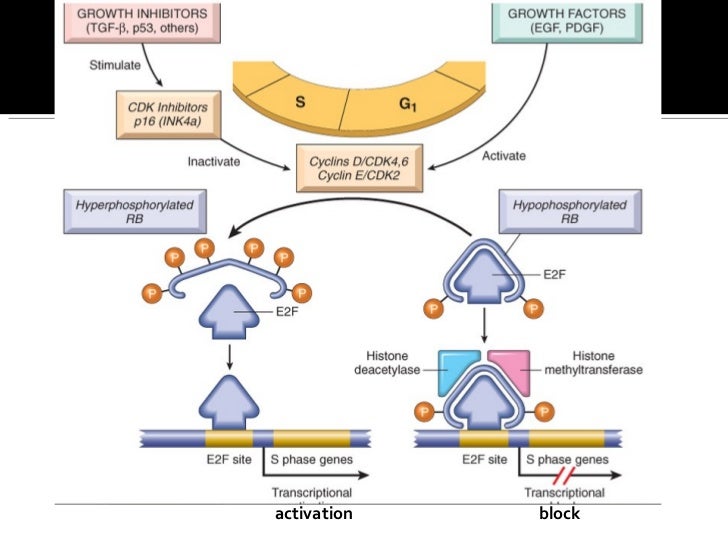
The retinoblastoma (Rb) protein coupled with the E2F transcription factor family was demonstrated to have roles in co … The Role of Retinoblastoma Protein in Cell Cycle Regulation: An Updated Review Curr Mol Med. 2021;21(8):620-629. doi: 10.2174/1566524020666210104113003. The Rb protein is a tumor suppressor, which plays a pivotal role in the negative control of the cell cycle and in tumor progression. It has been shown that Rb protein (pRb) is responsible for a
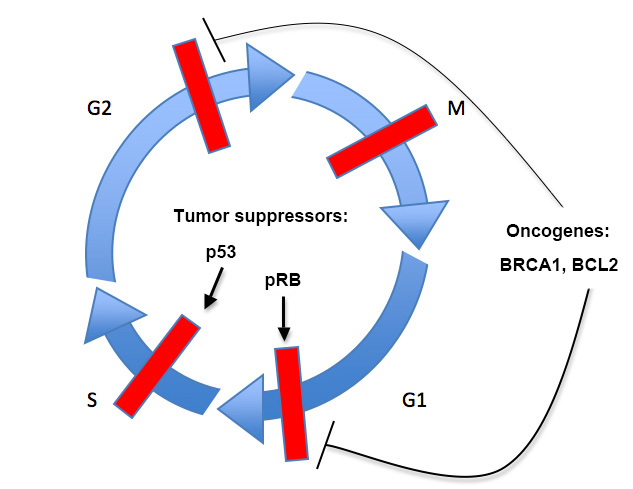
The Retinoblastoma Protein: a Master Tumor Suppressor Acts As a Link ... Biology Diagrams
Abstract. RB1 was the first tumor suppressor gene discovered. Over four decades of work have revealed that the Rb protein (pRb) is a master regulator of biological pathways influencing virtually every aspect of intrinsic cell fate including cell growth, cell-cycle checkpoints, differentiation, senescence, self-renewal, replication, genomic stability and apoptosis. The life history of cancer cells encompasses a series of genetic missteps in which normal cells are progressively transformed into tumor cells that invade surrounding tissues and become malignant. Most prominent among the regulators disrupted in cancer cells are two tumor suppressors, the retinoblastoma protein (RB) and the p53 transcription factor. Here, we discuss interconnecting signaling

The retinoblastoma (RB) family of proteins are found in organisms as distantly related as humans, plants, and insects. These proteins play a key role in regulating advancement of the cell division cycle from the G1 to S-phases. This is achieved through negative regulation of two important positive regulators of cell cycle entry, E2F transcription factors and cyclin dependent kinases.

Molecular mechanisms underlying RB protein function Biology Diagrams
The Rb protein is a tumor suppressor, which plays a pivotal role in the negative control of the cell cycle and in tumor progression. It has been shown that Rb protein (pRb) is responsible for a major G1 checkpoint, blocking S-phase entry and cell growth. The retinoblastoma family includes three memb …