44 The myc oncogene Types and their changes and role in tumours c Biology Diagrams Induction of cell proliferation by promoting G 1 to S-phase transition during cell cycle progression is one of Myc's best characterized functions, a feature linked to its pro‐oncogenic
We will review here the role of MYC as cell-cycle brake releaser i.e., how MYC stimulates cell cycle mainly through the repression of cell-cycle inhibitors . Cell-cycle progression is regulated by serine/threonine protein kinases composed by a catalytic subunit or CDK (cyclin-dependent protein kinase), and a regulatory subunit, the cyclin [ 43 The entry in cell cycle of quiescent cells upon Myc enforced expression has been described in many models. Also, the downregulation or inactivation of Myc results in the impairment of cell cycle progression. Given the frequent deregulation of Myc oncogene in human cancer it is important to dissect out the mechanisms underlying the role of Myc
myc expression on cell cycle progression Biology Diagrams
The timing of cyclin E induction was the earliest observable effect of reduced Myc expression. Our data indicate that Myc contributes to regulation of proliferation by a cell-autonomous mechanism that involves the modulation of cyclin E expression and, consequently, progression through the restriction point of the cell cycle. An indirect proof of the role of Myc in cell cycle progression is the fact that Mxd proteins (Mxd1, Mxi1, Mxd3, Mxd4 and Mnt), which bind to Myc-binding sites and antagonize Myc transcriptional activity, inhibit cell proliferation (reviewed in [80], [81], [82]). Cell cycle arrest is also observed upon the enforced expression of MadMyc, a

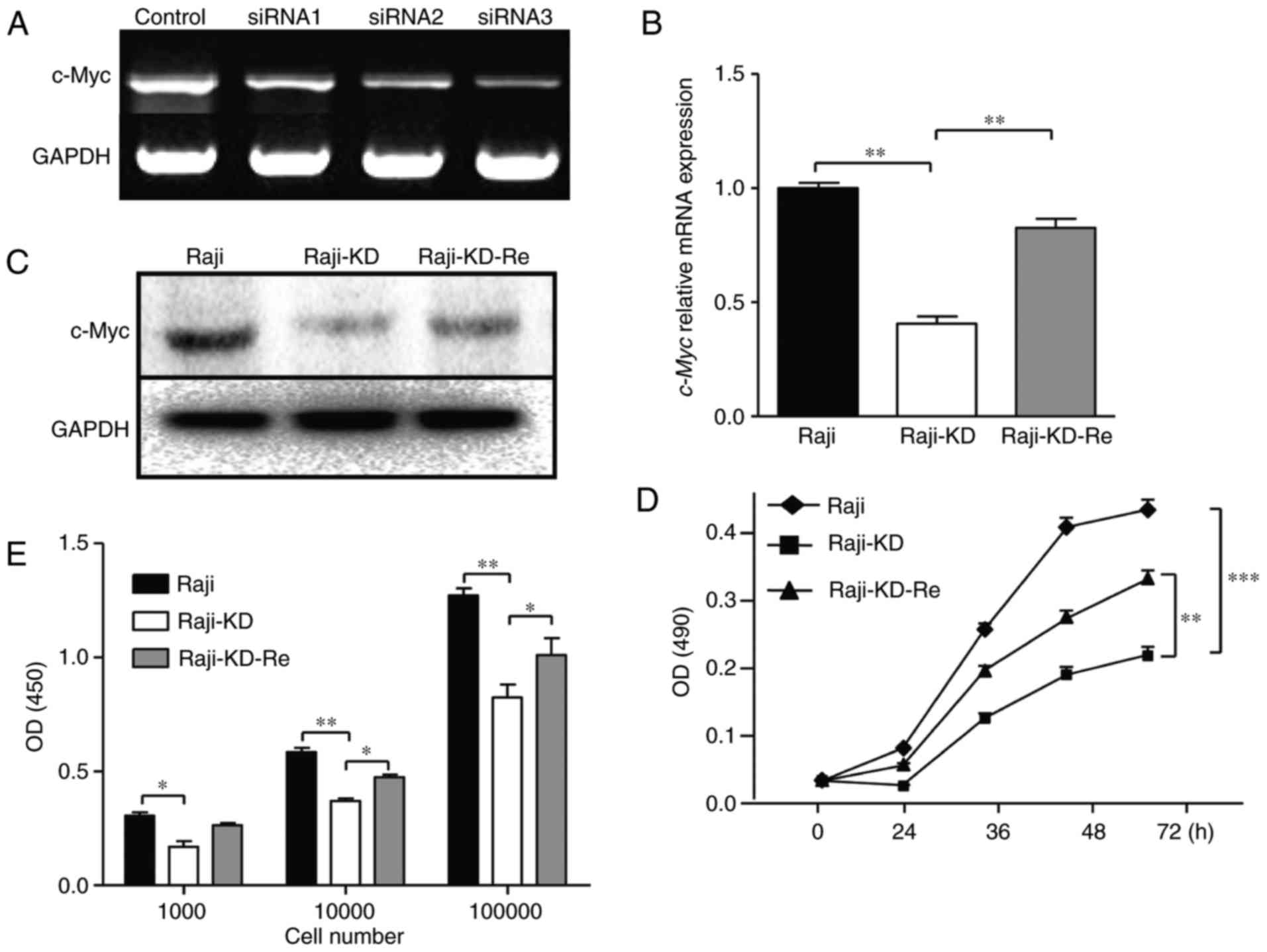
In the present study, a c‑Myc‑knockdown model (Raji‑KD) was established using Raji cells, and it was indicated that c‑Myc regulates the expression of genes associated with cell cycle progression in G2/M‑phase, cyclin D kinase (CDK)1 and cyclin B1, by modulating 60 kDa Tat‑interactive protein (TIP60)/males absent on the first (MOF We further show that heterogeneity in c-Myc dynamics leads to variable target gene transcription and that timing of c-Myc expression predicts cell-cycle progression rates and drug sensitivities. Together, our data advocate for a model in which cancer cells increase the heterogeneity of functionally diverse transcription factors such as c-Myc to

MYC Oncogene Contributions to Release of Cell Cycle Brakes Biology Diagrams
A large body of physiological evidence shows that either upregulation or downregulation of intracellular c-Myc activity has profound consequences on cell cycle progression. Recent work suggests

c-Myc affects cell cycle progression at multiple independent points. It is often observed that a single primary regulatory defect can elicit pleiotropic phenotypes by a cascade of downstream effects. For example, c-Myc could act primarily at the point of Cdk4 and -6 activation but cause more generalized effects by interfering with the